WVPBRN project sets sights on preventing blindness in diabetic patients
When people think about the treatment and management of their diabetes, A1C tests and foot exams usually come to mind. Often overlooked is the recommended retinal eye exam. This eye exam is crucial because many West Virginians with diabetes are at risk for blindness caused by diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause of blindness in the U.S. for people ages 20 to 65. It is now projected that one in three Americans with diabetes will experience diabetic retinopathy by the year 2050. While the projection may be frightening, early detection reduces the risk of severe vision loss by 90 percent.
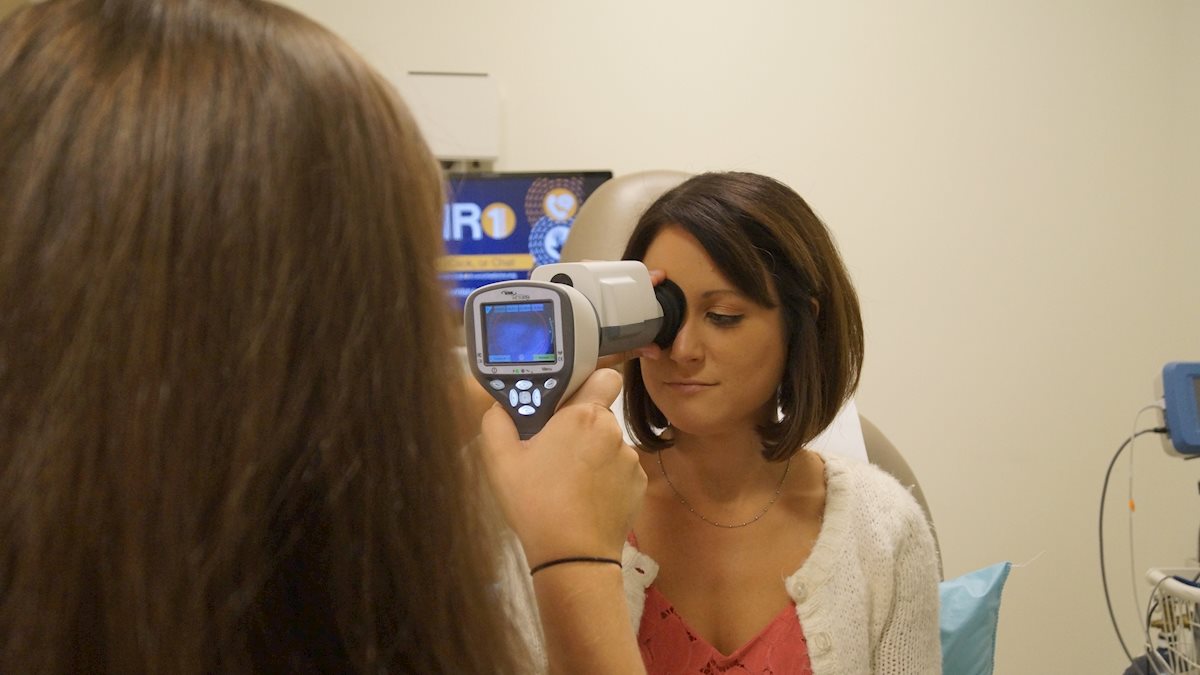
This critical need for early detection and prevention of diabetic retinopathy is the key mission of the West Virginia Practice-Based Research Network’s (WVPBRN) Sight Outreach Program. The program trains primary care clinical staff members across the state to use the Intelligent Retinal Imaging System (IRIS) to quickly capture images of the patient’s retinas.
“Patients with diabetes are supposed to get an eye evaluation annually, however, in West Virginia only about 60% received eye care in the past year,” said William Lewis, M.D., family medicine physician at Harper’s Ferry Family Medicine and WVPBRN co-director. “This IRIS program removes barriers to access that often prevent people from getting these exams and can help us bring the best care possible to persons with diabetes.”
The speed and ease of use makes the IRIS program convenient for both providers and patients. During routine primary care visits in participating clinics across the state, providers take a photograph of the patient’s retina. This finely detailed image is then securely transmitted to a retinal specialist at the WVU Eye Institute. The entire procedure takes less than five minutes for most patients.
After receiving the images, ophthalmologists analyze them for any evidence of ophthalmic pathology and deliver results directly to the patient’s electronic medical record. The primary care providers also receive recommended care plans and referral paths if indicated.
“IRIS not only helps us treat our patient’s eyes, it helps us comprehensively treat the whole patient,” said Lewis. “If we detect early-stage retinopathy, we know we need to be more aggressive with the management of our patient’s diabetes.”
To date, more than 5,400 patients have been screened across the 10 participating WVPBRN sites, including WVU Medicine outpatient clinics in Morgantown, Fairmont, Reedsville, and Harpers Ferry; as well as multiple Community Care of West Virginia and Valley Health Systems sites. Of those, approximately 21% had evidence of diabetic retinopathy. Moreover, the IRIS scan detected other ophthalmic pathology such as glaucoma, cataracts, or macular degeneration in 28% of scanned patients.
The data provided by the project not only led to patient improvements, but also impacted practice and policy across the state. IRIS results have influenced West Virginia Medicaid, the Public Employees Insurance Agency (PEIA), and Highmark policies.
“I cannot state enough regarding the positive impact that this program is having for West Virginia residents,” said Sally Hodder, M.D., WVCTSI director and associate vice president for clinical and translational science at WVU. “Not only is it preventing blindness and improving outcomes for diabetic patients, but the practice and policy changes that have been generated will improve early detection of ophthalmic pathology in the future.”
WVCTSI Background
WVCTSI is funded by an IDeA Clinical and Translational grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (U54GM104942) to support the mission of building clinical and translational research infrastructure and capacity to impact health disparities in West Virginia.
im/1/14/20